Understanding the Different Types of Home Heating Systems
When it comes to heating your home, you've got several options. Traditional forced-air furnaces are reliable and efficient, while boiler-based systems provide even heating. Electric baseboards are easy to install but may not be the most cost-effective. Radiant floor heating offers comfortable, energy-efficient warmth, while heat pumps are versatile for both heating and cooling. Geothermal systems are highly efficient but require significant upfront investment. Ductless mini-splits provide flexible heating and cooling without ductwork. And hybrid systems combine the best of multiple technologies to optimize performance and savings. To dive deeper into the pros and cons of each, keep reading.
Key Takeaways
- Homeowners have a range of heating system options including forced-air furnaces, boilers, electric baseboards, radiant floor heating, and heat pumps.
- Hybrid heating systems combine a high-efficiency furnace or boiler with a heat pump, leveraging heat pump efficiency in milder weather.
- Hybrid systems require careful system design and installation considerations to optimize performance and reduce energy consumption.
- Factors to consider in hybrid system selection include energy efficiency, installation costs, available space, noise levels, and maintenance requirements.
- Consulting with qualified HVAC professionals is recommended for informed decision-making when selecting the most suitable heating system for a home.
Traditional Forced-Air Furnaces
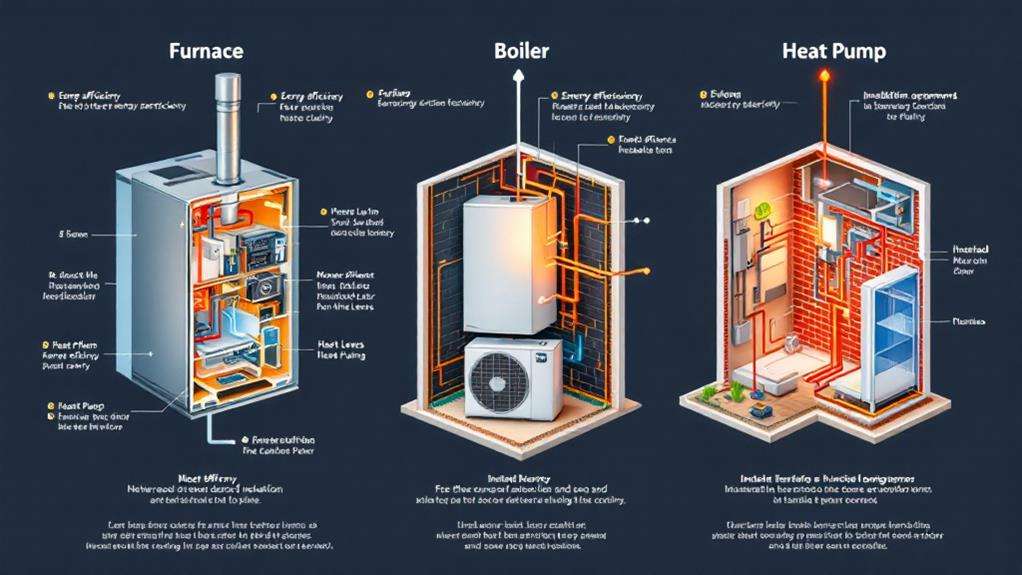
The traditional forced-air furnace is a widely used home heating system. It's a reliable and efficient way to keep your home warm during the colder months. These furnaces use a blower to circulate heated air through a network of ducts, delivering warmth to each room. Their energy efficiency has improved over the years, making them a cost-effective option for many homeowners.
Maintaining a forced-air furnace is relatively straightforward. Regular filter changes and periodic tune-ups by a professional can help ensure your system runs smoothly and efficiently. This helps to extend its lifespan and prevent costly breakdowns. Additionally, properly sealing and insulating your ductwork can improve the overall performance of your furnace, further enhancing its energy efficiency.
While there are other heating options available, the traditional forced-air furnace remains a popular choice for its reliability, efficiency, and ease of maintenance. With proper care and attention, this system can keep your home cozy and comfortable for years to come.
Boiler-Based Heating Systems
While forced-air furnaces are a popular choice, boiler-based heating systems offer an alternative approach to keeping your home warm. Boiler-based systems use a central boiler to heat water, which is then circulated through a network of pipes to radiators or baseboards throughout your home. This type of system can be highly efficient, with boiler types ranging from traditional cast-iron models to more modern, high-efficiency condensing boilers.
Boiler-based systems often provide more even and consistent heating compared to forced-air systems, as the heat is distributed through the water rather than blown through ductwork. Additionally, boilers generally have a longer lifespan than furnaces, making them a reliable long-term investment. When it comes to heating efficiency, modern boiler systems can achieve AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) ratings of 90% or higher, meaning they convert a significant portion of their fuel into usable heat for your home.
Electric Baseboard Heating

Another option for home heating is electric baseboard heating. These systems use electric resistance coils installed along the baseboards to warm the air in a room. They're easy to install and don't require ductwork, making them a great choice for homes without existing HVAC systems. The energy efficiency of electric baseboard heaters can vary, but they generally have lower upfront costs than other heating systems.
The installation requirements for electric baseboard heaters are relatively straightforward. They're wall-mounted units that simply need to be plugged into a standard electrical outlet. This makes them a DIY-friendly option for many homeowners. However, it's important to ensure the electrical system in your home can handle the additional load of the heaters. Improper installation or overloading the electrical circuit can create safety hazards.
Radiant Floor Heating
Radiant floor heating systems provide a unique approach to home heating. Unlike traditional forced-air systems, radiant floor heating uses a network of pipes or cables installed beneath your floors to evenly distribute warmth throughout your living space. This even heat distribution ensures every corner of your home stays comfortable, without the cold spots or drafts common with other heating methods.
What makes radiant floor heating so efficient? The system warms the floor itself, which then radiates heat upwards, providing a gentle, consistent temperature. This efficient energy usage means you'll use less fuel to maintain your desired comfort level, translating to significant savings on your utility bills. Additionally, radiant floor heating is very quiet, with no noisy fans or ducts to disturb your home's ambiance.
If you're looking for a comfortable, energy-efficient heating solution, radiant floor heating is definitely worth considering for your home.
Air-Source Heat Pumps

Air-source heat pumps offer a versatile heating and cooling solution for your home. They utilize advanced technology to efficiently transfer heat between the indoor and outdoor air, allowing them to both heat and cool your living spaces. Their seasonal efficiency ratings, which measure their performance across an entire heating or cooling season, make them a cost-effective choice compared to traditional furnaces or air conditioners.
Installing an air-source heat pump requires careful consideration of your home's layout and insulation. Proper placement of the outdoor unit and indoor air handler is crucial for optimal performance. Additionally, you'll need to ensure your home's electrical system can handle the pump's power requirements. When installed correctly, air-source heat pumps offer a reliable and energy-efficient way to maintain a comfortable temperature in your home year-round.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
While air-source heat pumps rely on outdoor and indoor air to transfer heat, geothermal heat pumps use the stable temperatures found underground or in a nearby water source. These ground-source systems offer exceptional efficiency, as they can extract heat from the earth or a water body, even when outside temperatures are frigid. The ground maintains a relatively constant temperature just a few feet below the surface, making it an ideal heat source or sink for your home's heating and cooling needs.
When it comes to installation considerations, geothermal heat pumps require more extensive groundwork, such as drilling or trenching, to access the underground or water-based heat source. However, the long-term energy savings and reduced environmental impact often outweigh the higher upfront costs. Additionally, geothermal systems have fewer moving parts, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and an extended lifespan compared to traditional HVAC systems.
Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps

Ductless mini-split heat pumps offer a flexible and efficient alternative to traditional HVAC systems. These compact, wall-mounted units don't require ductwork, making them ideal for homes without existing ductwork or where adding ducts would be impractical. Ductless systems work by using an outdoor compressor unit connected to one or more indoor air-handling units, allowing you to heat and cool specific rooms or zones as needed.
One of the key advantages of ductless mini-splits is their impressive energy efficiency. By eliminating ductwork, you avoid the energy losses associated with forced-air systems, potentially reducing your heating and cooling costs by up to 30%. Additionally, the advanced technology in ductless systems, such as inverter compressors, ensures optimal energy savings potential. You can further enhance the efficiency by selecting models with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings.
Ductless mini-splits provide a versatile and energy-efficient solution for your home's heating and cooling needs, allowing you to precisely control the comfort in each room.
Hybrid Heating Systems
Amid the array of home heating options, hybrid heating systems have emerged as an intriguing choice, blending the efficiency of modern technologies. These systems seamlessly combine the strengths of different heating sources, often pairing a high-efficiency furnace or boiler with a heat pump, to provide year-round comfort and energy savings.
- Hybrid heating systems leverage the efficiency of heat pumps during milder weather, while relying on the supplemental heating of a furnace or boiler during colder months, optimizing performance and reducing energy consumption.
- The installation requirements for hybrid systems can be more complex than traditional heating options, often necessitating the integration of multiple components and specialized expertise.
- Homeowners can benefit from the enhanced energy efficiency and versatility of hybrid systems, which can adapt to changing weather conditions and provide both heating and cooling capabilities.
- Careful consideration of climate, home size, and budget is crucial when selecting the right hybrid heating system to ensure maximum comfort and cost-savings.
- Ongoing maintenance and professional service are essential to maintain the optimal performance and longevity of hybrid heating systems.
Factors to Consider
When selecting a hybrid heating system, several key factors should be carefully evaluated to ensure the best fit for your home and needs. Energy efficiency should be a top priority, as hybrid systems can significantly reduce your heating costs by optimizing the use of multiple energy sources. The installation costs are another crucial consideration, as the upfront investment can vary widely depending on the specific system and your home's existing infrastructure.
Additionally, you'll want to assess the available space in your home to accommodate the hybrid system's components. Factors like noise levels, maintenance requirements, and the system's compatibility with your home's existing cooling system should also be taken into account. Consulting with a qualified HVAC professional can help you weigh these factors and make an informed decision that balances your budget, energy needs, and long-term cost savings.
