How to Safely Remove Rust From Metal Pipes
To safely remove rust from metal pipes, start by evaluating the severity of the corrosion. Wear protective gear like gloves, goggles, and a mask before beginning. You can use chemical rust removers, following manufacturer instructions carefully, or opt for mechanical methods like wire brushing or sanding. For a gentler approach, try natural solutions such as white vinegar or a baking soda paste. After removing the rust, rinse and dry the pipes thoroughly. Apply a rust-inhibiting coating to prevent future oxidation. Remember to work in a well-ventilated area and dispose of any chemicals properly. With the right techniques, you'll be on your way to rust-free pipes in no time.
Understanding Rust Formation
Nearly all metal pipes are susceptible to rust formation, a process known as oxidation. When exposed to oxygen and moisture, the iron in metal pipes reacts, forming iron oxide—commonly known as rust. Understanding this process is indispensable for effective rust prevention and removal.
Several metal corrosion factors contribute to rust formation. The primary culprits are water, oxygen, and electrolytes. Water acts as a catalyst, while oxygen is necessary for the oxidation reaction. Electrolytes, such as salt, accelerate the process by increasing electrical conductivity. Temperature fluctuations and humidity levels also play prominent roles in rust development.
Different types of metal oxides can form depending on the specific metal and environmental conditions. For iron-based metals, the most common form is red rust (Fe2O3). However, you may encounter other variants like black rust (Fe3O4) or yellow rust (FeO(OH)). Each type has distinct characteristics and may require different removal techniques.
To effectively combat rust, you'll need to address these underlying factors. Controlling moisture exposure, using protective coatings, and maintaining proper ventilation can greatly reduce the likelihood of rust formation on your metal pipes.
Safety Precautions
Before tackling rust removal, it is crucial to prioritize safety. When working with rust and chemicals, you're exposed to potential hazards that require careful consideration. Start by guaranteeing proper ventilation in your work area. Open windows and doors, or use fans to circulate air and prevent the buildup of fumes.
Protect yourself with the right protective equipment. Wear safety goggles to shield your eyes from debris and chemicals. Don a pair of chemical-resistant gloves to safeguard your hands from corrosive substances and sharp rust particles. If you're using power tools or creating dust, wear a respirator mask to avoid inhaling harmful particles.
Dress in long sleeves and pants to minimize skin exposure. Keep a first aid kit nearby in case of accidents. When using chemical rust removers, carefully read and follow the manufacturer's instructions. Store these products safely out of reach of children and pets. If you're working with electrical tools, make sure they're properly grounded and keep them away from water sources. Finally, always work in a well-lit area to avoid mishaps and improve accuracy in your rust removal efforts.
Assessing Rust Severity
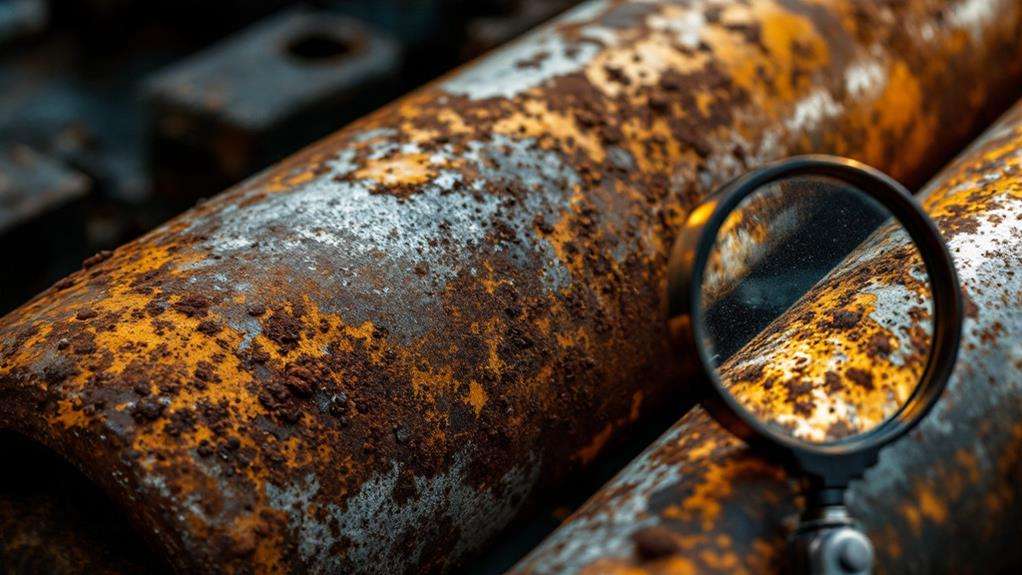
The cornerstone of effective rust removal is accurately evaluating the severity of the problem. Before you begin any rust removal process, it's imperative to assess the extent of rust on your metal pipes. This step will help you determine the most appropriate method for removal and whether the pipe's structural integrity has been compromised.
When examining rust severity, consider the following factors:
- Surface area affected: Determine what percentage of the pipe is covered in rust.
- Depth of corrosion: Check if the rust is superficial or has penetrated deeper into the metal.
- Age of the pipe: Older pipes may have more extensive damage beneath the surface.
- Environmental conditions: Consider the pipe's exposure to moisture, chemicals, or other corrosive elements.
Start by visually inspecting the pipe, looking for signs of pitting, flaking, or discoloration. Use a wire brush to gently scrape the surface, revealing the true extent of the rust. If you're unsure about the pipe's structural integrity, it's best to consult a professional. They can help you determine if the pipe needs replacement or if rust removal is sufficient. Remember, accurately evaluating rust severity is key to choosing the right treatment method and ensuring the longevity of your metal pipes.
Chemical Rust Removal Methods
Once you've assessed the rust severity, chemical rust removal methods offer an effective solution for treating corroded metal pipes. These methods involve using specialized products designed to dissolve rust and restore the metal surface. Before starting, guarantee you're working in a well-ventilated area and wearing appropriate protective gear.
Common chemical rust removers include phosphoric acid-based solutions, oxalic acid, and citric acid. Apply the chosen product according to the manufacturer's instructions, typically by brushing or spraying it onto the rusted areas. Allow the solution to work for the recommended time, which can range from 15 minutes to several hours, depending on the product and rust severity.
After the treatment, thoroughly rinse the pipes with water and dry them completely. It's essential to follow proper disposal methods for used chemicals and contaminated rinse water. Check local regulations for guidance on safe disposal practices.
Always prioritize hazard identification when working with chemical rust removers. Read product labels carefully, noting any specific precautions or handling instructions. If you're unsure about using chemical methods or dealing with extensive rust damage, consider consulting a professional plumber for advice or assistance.
Mechanical Rust Removal Techniques

Three primary mechanical rust removal techniques can effectively tackle corrosion on metal pipes without chemicals. The first method involves using abrasive cleaning tools like wire brushes, sandpaper, or steel wool to manually scrub away rust. You'll need to apply significant elbow grease, but it's an affordable and accessible option for small-scale projects.
The second technique is power tool-assisted abrasion. Electric sanders, grinders, or wire brush attachments for drills can speed up the process and tackle more stubborn rust. However, be careful not to damage the underlying metal when using these powerful tools.
High-pressure water blasting is the third method, ideal for larger areas or hard-to-reach spots. This technique uses a concentrated stream of water to blast away rust and debris, leaving a clean surface behind.
When choosing a mechanical rust removal technique, consider:
- The extent of rust damage
- The size and accessibility of the affected area
- Your available tools and budget
- The pipe material's durability
Remember to wear proper protective gear, including gloves, safety glasses, and a dust mask, when using any of these methods. After removing the rust, apply a protective coating to prevent future corrosion.
Natural Rust Removal Solutions
While mechanical methods are effective, you might prefer a gentler approach to rust removal. Natural solutions offer eco-friendly cleaners and homemade remedies that can effectively tackle rust on metal pipes.
One popular natural option is white vinegar. Soak the rusted area in vinegar for several hours or overnight, then scrub with a wire brush. For stubborn rust, create a paste using baking soda and water. Apply it to the affected area, let it sit for a few hours, and then scrub it off.
Lemon juice is another acidic solution that can dissolve rust. Apply fresh lemon juice to the rusted surface, sprinkle salt over it, and let it sit for a few hours before scrubbing. Alternatively, use potato and salt: cut a potato in half, dip the cut side in salt, and rub it on the rust. The oxalic acid in the potato combined with salt creates a mild abrasive effect.
For larger areas, try a salt and lime juice mixture. Sprinkle salt over the rusted surface, squeeze lime juice over it, and let it sit for a few hours before scrubbing.
Preventing Future Rust Formation

After removing rust from your metal pipes, it is imperative to focus on preventing its recurrence. Proper pipe coatings play a pivotal role in safeguarding against future rust formation. Apply a rust-inhibiting primer and paint specifically designed for metal surfaces to create a protective barrier. Don't forget to coat both the interior and exterior of the pipes for extensive protection.
Periodic inspection is key to catching rust early and preventing extensive damage. Establish a regular maintenance schedule to examine your pipes for signs of corrosion or wear. During these checks, look for:
- Discoloration or flaking paint
- Pitting or roughness on the surface
- Accumulation of moisture or condensation
- Weak spots or thinning areas in the pipes
Address any issues immediately to prevent rust from spreading. Keep the area around your pipes dry and well-ventilated, as moisture is a primary catalyst for rust formation. If your pipes are in a humid environment, consider using a dehumidifier to reduce ambient moisture. Additionally, insulate exposed pipes to minimize temperature fluctuations that can lead to condensation. By implementing these preventive measures, you'll greatly extend the life of your metal pipes and reduce the need for future rust removal.
When to Replace Rusty Pipes
Despite your best efforts at prevention and maintenance, there may come a time when replacing rusty pipes is the only viable option. Knowing when to make this decision is imperative for maintaining the integrity of your plumbing system and avoiding potential water damage or health hazards.
Consider pipe replacement when you notice:
- Extensive surface rust covering large areas
- Visible holes or cracks in the pipes
- Frequent leaks or water pressure issues
- Discolored or foul-smelling water
- Pipes that are over 50 years old
When evaluating pipe lifespan estimation, factor in the material type. Galvanized steel pipes typically last 20-50 years, while copper pipes can endure 50-70 years. PVC pipes have a lifespan of 25-40 years. If your pipes are approaching or exceeding these ranges, replacement may be necessary.
Before deciding on replacement, consult a professional plumber for a thorough inspection. They can assess the extent of damage and provide expert recommendations. Remember, while replacing pipes can be costly, it's often a worthwhile investment to prevent more extensive damage and guarantee the long-term health and safety of your plumbing system.
Maintaining Rust-Free Pipes

Maintaining rust-free pipes is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and regular care. To extend your pipe lifespan and implement effective corrosion mitigation strategies, you'll need to adopt a proactive approach. Regularly inspect your pipes for signs of rust or damage, and address any issues promptly. Keep your pipes dry whenever possible, as moisture is a primary catalyst for rust formation.
Consider applying protective coatings to your pipes, such as rust-resistant paint or specialized sealants. These can create a barrier against moisture and other corrosive elements. Additionally, maintain proper water chemistry in your plumbing system to minimize the risk of internal corrosion.
Here are four key steps to maintain rust-free pipes:
- Monitor water pressure and flow rates
- Clean pipes regularly to remove debris and mineral buildup
- Address leaks immediately to prevent moisture accumulation
- Install water softeners if you have hard water
