Understanding Toilet Flush Mechanisms: What You Need to Know

Toilet flush mechanisms are crucial for efficient waste removal and maintaining bathroom hygiene. You'll find two main components: the bowl and tank. When you press the flush handle, it lifts the flapper, releasing water from the tank into the bowl. This creates a powerful suction that removes waste. Various types of flush systems exist, including gravity, pressure-assisted, and dual flush. Key components like the fill valve, flush valve, and flapper work together to ensure proper function. Common issues include weak flushing and continuous running, often solved by simple maintenance. Understanding these basics can help you troubleshoot problems and optimize your toilet's performance. Dive deeper to uncover the intricate workings of this everyday essential.
Key Takeaways
- Toilet flush mechanisms consist of a tank, bowl, and key components like the fill valve, flush valve, and flapper.
- Pressing the flush handle lifts the flapper, releasing water from the tank to create suction in the bowl.
- Different types of flush systems include gravity, pressure-assisted, dual flush, and tornado flush toilets.
- Common flushing problems include weak flushes, continuous running, and issues with flappers or chains.
- Regular maintenance and cleaning of toilet parts help maintain optimal flushing performance and efficiency.
The Anatomy of a Toilet
Every toilet consists of two main components: the bowl and the tank. The bowl is where waste is deposited, while the tank serves as a water reservoir for flushing. Inside the tank, you'll find several crucial parts that work together to create an effective flush mechanism.
The tank's primary function is to hold water and rapidly discharge it during a flush. This quick release of water, typically occurring within 3 seconds, creates a powerful siphon effect that removes waste from the bowl. Key components within the tank include the fill valve, flush valve (also known as the flapper), flush handle, and a chain connecting the flapper to the handle.
When you press the flush handle, it lifts the flapper, allowing water to rush from the tank into the bowl. This sudden influx of water generates suction, effectively evacuating waste. Once the flush is complete, the fill valve activates to replenish the tank's water supply. As the water level rises, it lifts a float, which signals the fill valve to shut off when the appropriate water level is reached, preparing the toilet for its next use.
How Flush Mechanisms Function
Almost all flush mechanisms operate on a simple yet effective principle. When you press the flush handle, it lifts the flapper, which opens the flush valve. This action allows water to rush from the tank into the bowl, creating a powerful suction that removes waste. As the water level in the tank drops, the float descends, triggering the fill valve to replenish the tank for the next flush.
The flapper plays a crucial role in this process. It seals the flush valve between flushes, preventing water from continuously draining into the bowl. Once the flush is complete, the flapper returns to its closed position, allowing the tank to refill.
To better understand the flush mechanism, consider these key components:
- Flush valve: Controls the water flow from tank to bowl
- Flapper: Seals the flush valve and initiates the flush when lifted
- Fill valve: Refills the tank after each flush
Types of Toilet Flush Systems
Within the world of toilet technology, several distinct flush systems have emerged to meet various needs and preferences. You'll find gravity flush systems, which rely on the weight of water in the tank to create siphonic suction and evacuate the bowl. These are common in many households due to their simplicity and reliability.
If you're looking for a more powerful flush, pressure-assisted toilets might be your best bet. They use compressed air to forcefully push water into the bowl, ensuring a thorough clean with each flush. For those concerned about water conservation, dual flush systems offer separate options for liquid and solid waste, allowing you to use only the necessary amount of water.
Tornado flush toilets create a powerful swirling action that efficiently cleans the bowl while using water effectively. This innovative design combines thorough cleaning with water savings. If you're interested in an eco-friendly option that doesn't use water at all, composting toilets break down waste naturally without flushing. These systems are ideal for off-grid locations or those looking to minimize their environmental impact.
Key Components and Their Roles
Delving into the inner workings of a toilet reveals several key components that work together to create an efficient flush. The toilet tank, which holds the water for flushing, is the starting point of this process. When you press the flush lever, it activates the flapper valve, allowing water to flow from the tank into the bowl.
The flush valve plays a crucial role in controlling this water flow, ensuring that the right amount is released for effective waste removal. As water enters the bowl, it triggers the siphon effect, creating suction that swiftly carries away waste.
To prevent overflows, the overflow tube acts as a safeguard, directing excess water into the bowl if the fill valve malfunctions. Meanwhile, the float mechanism regulates the water level in the tank, ensuring it refills properly after each flush.
Understanding these components can help you:
- Troubleshoot common toilet issues
- Perform basic maintenance tasks
- Appreciate the engineering behind this everyday fixture
Common Flushing Problems and Solutions
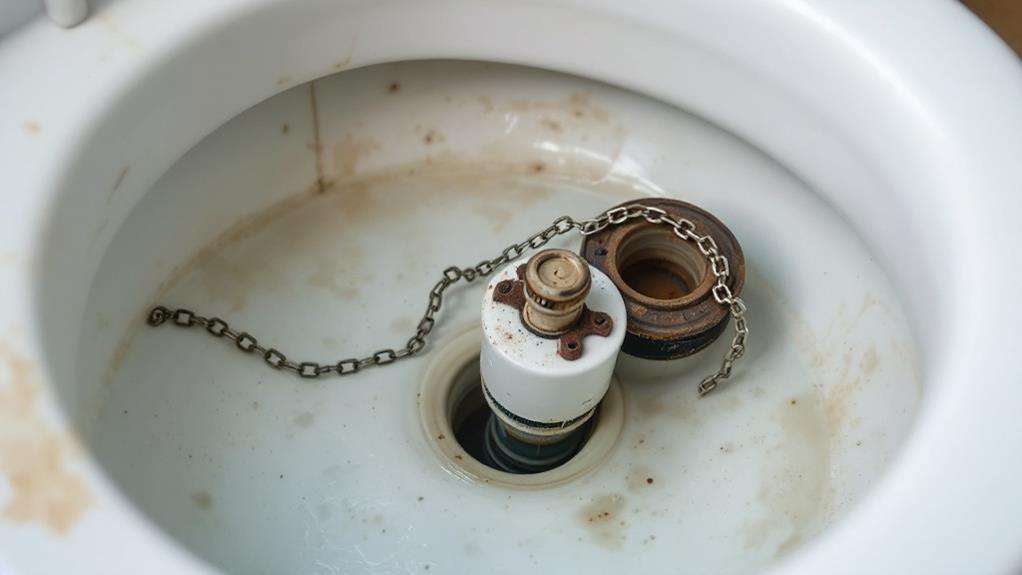

Identifying common flushing problems can save you time and money on unnecessary plumbing calls. Weak flushing is often caused by clogged water jets, which you can resolve by regularly cleaning them. If you're experiencing weak flushing or a running toilet, adjusting the water level in the tank might be the solution. Simply check the fill line and adjust accordingly.
A continuously running toilet is another frequent issue. To address this, inspect the flapper and float. If they're worn or damaged, replacing them can solve the problem. Similarly, replacing other worn parts like the fill valve can fix various flushing issues.
Don't forget to check the handle and its connection to the flapper. A loose or improperly adjusted chain can prevent proper flushing. Tighten it if necessary, ensuring there's enough slack for the flapper to seal completely.
Lastly, ensure all components are properly installed and connections are tight. This not only prevents flushing problems but also extends your toilet's lifespan. By understanding these common issues and their solutions, you'll be better equipped to maintain your toilet's flush mechanism and avoid costly repairs.
Optimizing Flushing Power and Efficiency
Efficiency is key when it comes to optimizing your toilet's flushing power. By understanding various flush systems and making simple adjustments, you can significantly improve your toilet's performance while conserving water. Dual-flush toilets offer an excellent solution, allowing you to choose between different water volumes for liquid and solid waste.
For single-flush toilets, adjusting the fill valve can help optimize the water level and flushing performance. Ensure that the water level drops to the appropriate height after each flush, as this impacts the toilet's efficiency. High-quality flush valve components are crucial for consistent and powerful flushing, so consider upgrading if necessary.
To further enhance your toilet's flushing power and efficiency:
- Regularly maintain and clean your toilet parts to prevent clogs and ensure smooth operation
- Choose a toilet model with advanced features like tornado flush technology for improved efficiency
- Properly install and adjust all components to reduce noise and extend your toilet's lifespan
Evolution of Flush Technology

Flush technology has come a long way since the early days of gravity-based systems. You'll find that modern toilet flush systems offer improved performance, water efficiency, and easier maintenance compared to their predecessors.
The evolution of flush technology began with simple gravity flush mechanisms, which relied solely on the force of falling water to remove waste. As demands for better performance grew, tank-based gravity flush systems emerged, providing more consistent flushing power.
A significant advancement came with the introduction of pressure-assisted flush toilets. These systems use compressed air to force water into the bowl with greater force, resulting in a more powerful and effective flush.
Water conservation efforts led to the development of dual flush systems, allowing you to choose between two water volumes depending on the type of waste. This innovation helps you reduce water usage without sacrificing performance.
Perhaps the most radical change in flush technology is the composting toilet. This system breaks down waste through natural processes, eliminating the need for water altogether. While not suitable for all situations, composting toilets represent a significant step towards sustainable waste management.
