Everything You Need to Know About Circulator Pumps
Circulator pumps are essential components in heating and cooling systems, designed to move water or other fluids through closed loops. You'll find them in various types, including continuous, on-demand, and time-and-temperature models. These compact devices work by using centrifugal force to create pressure differentials, efficiently circulating heated water throughout your home. While they offer benefits like reduced water consumption and quick access to hot water, it's vital to ponder energy efficiency when selecting a pump. Proper installation and regular maintenance by a professional are key to maximizing performance and longevity. Comprehending the complexities of circulator pumps can help you make informed decisions for your home's comfort and efficiency.
What Are Circulator Pumps?
Workhorses of many heating and cooling systems, circulator pumps are compact devices designed to move water or other fluids through closed loop systems. These circulating pumps play a pivotal role in maintaining consistent temperatures and efficient energy transfer, particularly in hot water heating systems.
At their core, circulator pumps operate on centrifugal force principles. They feature an impeller that spins rapidly, creating pressure differentials that drive fluid movement. As the impeller rotates, it increases the velocity of the fluid, converting this kinetic energy into pressure energy. This process enables the pump to overcome system resistance and maintain a steady flow.
You'll often find circulator pumps in an inline configuration, meaning they're installed directly in the piping system. This setup allows for efficient fluid circulation without disrupting the overall system layout. By controlling the flow and pressure of the fluid, these pumps guarantee that heat is distributed evenly throughout your home or building.
Circulator pumps come in various sizes and capacities to suit different applications. They're indispensable for optimizing energy efficiency in heating and cooling systems, helping you maintain comfort while minimizing energy consumption.
Types of Circulator Pumps
Diving into the world of circulator pumps, you'll find several distinct types, each designed to meet specific needs and applications. The most basic are continuous circulation pumps, which constantly circulate water through your heating systems and pipes. While they guarantee hot water is always available, they're not the most energy-efficient option.
On the other hand, on-demand circulation pumps offer a more efficient solution. These pumps activate only when you need hot water, saving both energy and water. They're often equipped with switches or motion detectors to sense when water flow is required.
Time and temperature circulation pumps provide a middle ground. They operate at programmed times to deliver instant hot water, but they may lead to lukewarm water and potentially reduce pipe lifespan. However, when managed properly, they can save you money by running only when needed.
When choosing a circulator pump, consider your specific needs and usage patterns. Remember, professional installation is critical for any type of pump to guarantee proper functioning and avoid future issues. By selecting the right pump, you'll optimize your home's hot water delivery system, enhancing comfort and efficiency.
How Circulator Pumps Work
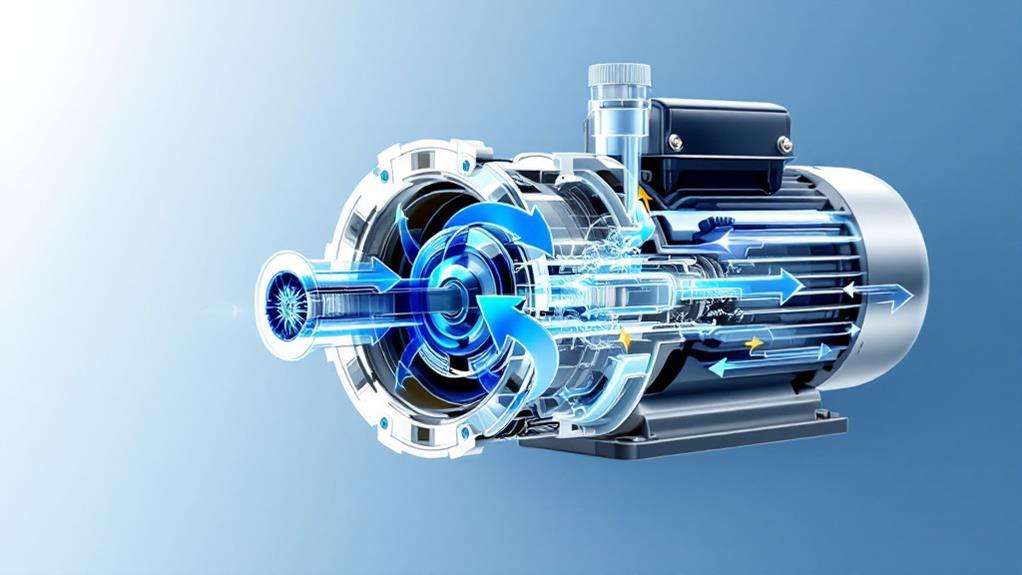
Now that you're familiar with the various types of circulator pumps, let's investigate how these devices actually function. At their core, circulator pumps are inline centrifugal pumps designed to move hot water through a heated circuit. The heart of the pump is the impeller, which is attached to a rotor inside the motor housing.
When you power on the circulating pump, the motor creates a rotating magnetic field that causes the rotor and impeller to spin. This rotation imparts kinetic energy to the water, creating a pressure differential that drives water circulation through the pipes. As the water exits the impeller at high velocity, it enters the volute channel surrounding it. This channel guides the water to the pump outlet while converting its kinetic energy into pressure.
You can control the pump's flow rate using the speed selector switch, which adjusts the motor's rotational speed. The pump's terminal box houses essential electrical connections, including ground, neutral, and line terminals. It also contains a capacitor that creates a "fake" second phase for the single-phase induction motor, ensuring smooth operation. Understanding these components helps you grasp how circulator pumps efficiently move water through your heating system.
Benefits of Circulator Pumps
Circulator pumps bring a host of benefits to your home's water heating system. These devices efficiently circulate heated water throughout your home, ensuring you have quick access to hot water whenever you need it. By reducing the time it takes for hot water to reach your taps, circulator pumps work to conserve a significant amount of water - up to 1000 gallons per person annually.
The impact converts the velocity of water flow into energy and water savings, leading to lower utility bills. You'll see a payback period of 2-6 years, after which you'll continue to reap the benefits for decades. Circulator pumps are essential components in hydronic heating systems and can help you migrate to cleaner, electrified water heating methods. They limit the inefficient operation of heat pump water heaters, further enhancing your home's energy efficiency.
Water circulation pumps also contribute to environmental conservation. With efficiency standards in place, these devices could save 5 million metric tons of CO2 by 2030 - equivalent to removing 1 million cars from the road for a year. By installing a circulator pump, you're not only improving your home's heated water circuit but also making a positive impact on the environment.
Energy Efficiency Considerations

While circulator pumps offer numerous benefits, it's important to select their energy efficiency implications. You might be surprised to learn that washing your hands can use more electricity than powering your refrigerator, due to the energy consumption of hot water circulator pumps. These pumps can increase your water heating energy use by up to 50%, with their annual electricity consumption potentially equaling that of two typical refrigerators.
Inefficient circulating pumps in heating systems can waste energy 24/7 through continuous operation. Even timer-controlled pumps run for 12-16 hours daily, hindering the migration to electrified, clean water heating. This inefficiency has a disproportionate impact on low-income households in apartments.
However, there's hope for improved efficiency. The Department of Energy has been working on energy efficiency standards since 2016, and California's SB 49 enables flexible demand appliance standards. These efforts could save 5 million metric tons of CO2 by 2030. By implementing standards, we can facilitate equitable access to efficiency and decarbonization. When evaluating circulator pumps for your hot water system, prioritize energy-efficient models to minimize your environmental impact and energy costs.
Installation and Maintenance
After considering energy efficiency, it's time to focus on proper installation and maintenance of circulator pumps. You'll want to hire a professional plumber for installation to guarantee exemplary performance and avoid future issues. They'll consider factors like pump size, system requirements, and pipe configuration to maximize efficiency.
Routine maintenance is essential for keeping your circulator pump running smoothly. Regularly check for leaks, clean the pump, and replace worn components. This will help extend the pump's lifespan and maintain its efficiency. Be aware that neglecting maintenance can lead to water damage, system malfunctions, and increased energy consumption.
To keep your hydronic heating or hot water system in top shape, monitor its performance regularly. Make adjustments as needed to maintain proper balance and efficiency. Remember, improper installation or maintenance can cause serious problems down the line. By taking a proactive approach to installation and maintenance, you'll ensure your circulator pump operates at peak performance for years to come. Don't hesitate to consult a professional if you're unsure about any aspect of your pump's care or operation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
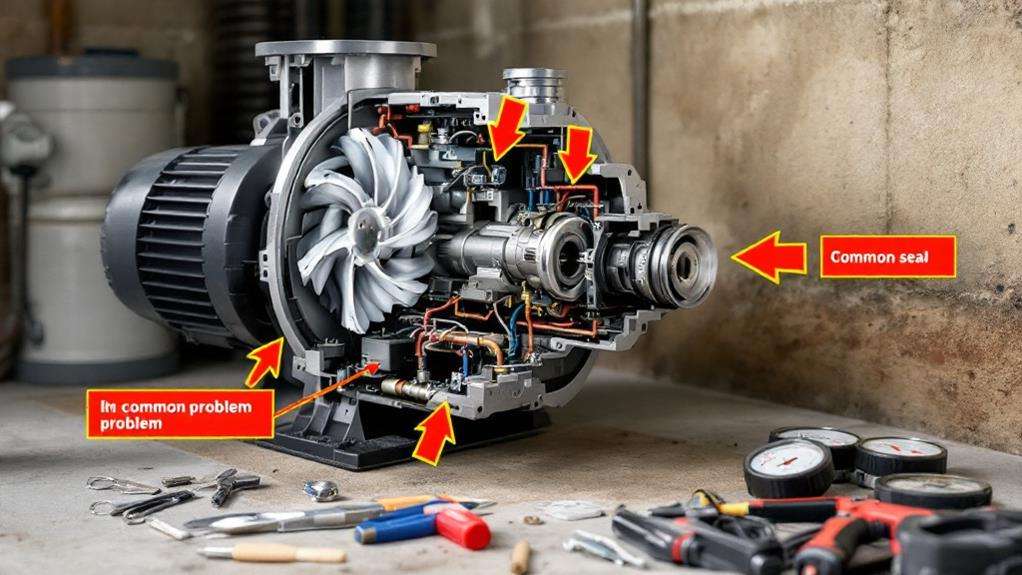
Even well-maintained circulator pumps can encounter issues. When troubleshooting, start by checking if the pump is receiving power and if the impeller within the pump is rotating freely. Listen for unusual noises that may indicate air in the system or a damaged bearing. If you're using inline centrifugal type pumps, guarantee the pump housing isn't cracked or leaking.
Check the inlet and outlet connections for blockages or restrictions. If there's no flow or low pressure at the outlet, inspect the impeller for damage or debris. High pressure at the pump's discharge might suggest a closed valve or obstruction downstream. If the motor is running hot, it could indicate overloading or faulty motor windings.
For circulating pumps used in heating systems, verify that air isn't trapped in the system, as this can prevent proper flow. If no flow develops despite the pump running, check for closed valves or a seized impeller. Remember to always disconnect power before opening the pump housing for internal inspection. If you're unsure about any troubleshooting steps, consult a professional to avoid damaging your system or voiding warranties.
Choosing the Right Circulator Pump
Selecting the right circulator pump is crucial for your system's efficiency and longevity. When choosing a pump, consider key factors like system size, pipe diameter, and heat load to guarantee optimal performance. Match the pump's capacity to your system's demands to avoid wasted energy and improve circulation.
Look for ENERGY STAR certified pumps, which can save you 35-80% in energy use compared to standard models. Variable-speed pumps are an excellent choice as they automatically adjust their output to match changing system needs, further enhancing efficiency.
The type and size of pump you select can drastically impact your system's overall performance. A properly sized pump will improve comfort, reduce operating costs, and extend your system's lifespan. Don't overlook the importance of pipe diameter when making your selection, as it directly affects flow rates and pressure.
