A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Well Pumps and Accessories
Well pumps are essential devices that move water from underground wells to your home. You'll encounter three main types: centrifugal, submersible, and jet pumps, each designed for different well depths. When choosing a pump, consider factors like well depth, water demand, and energy efficiency. Proper sizing is indispensable to ensure ideal performance and cost savings. Don't forget about essential accessories like pressure tanks, switches, and pitless adapters that help maintain a reliable water supply. Regular maintenance and troubleshooting knowledge will keep your system running smoothly. By understanding these basics, you'll be well-equipped to traverse the world of well pumps and their components.
What Are Well Pumps?
Well pumps are essential pieces of equipment for homes that rely on well water. These electromechanical devices are installed after drilling or digging a well to push water from the ground into your house. The main purpose of a well pump is to move water from the well through a jet or pipe and into a storage tank, ensuring a consistent water supply for your household needs.
Well pumps come in different sizes, depending on your property size, water usage, and the number of plumbing fixtures in your home. They're powered by electric motors that drive impellers or centrifugal pumps to create the necessary pressure for water extraction. When choosing a well pump, the most pivotal factor to ponder is the well depth, which you can determine using a simple string and bobber method.
There are three main types of well pumps: centrifugal pumps, submersible pumps, and jet pumps. Each type is designed for different well depths, with submersible pumps being ideal for deep wells, while jet pumps are better suited for shallow wells. Understanding your well's depth will help you select the most appropriate pump for your water system, ensuring efficient and reliable water supply to your home.
Types of Well Pumps
Now that you understand what well pumps are, let's investigate the different types available. Shallow well pumps, including centrifugal and jet pumps, are suitable for wells up to 25 feet deep. They're accessible above ground for easy maintenance but require priming to function. These pumps typically range from 3/4 to 1 HP and can provide 15-16 gallons per minute.
For deeper wells, submersible pumps are the go-to choice. They're installed underwater at the bottom of the well and can handle depths up to 325 feet. Submersible pumps push water upwards rather than drawing it by suction, with capacities ranging from 1/2 to 1 HP and supplying up to 26 gallons per minute.
Convertible jet pumps offer versatility, operating in both shallow (0-25 feet) and deep (25-90 feet) well configurations. By adjusting the ejector/jet portion, you can increase pressure to draw water from deeper depths.
When selecting a pump, consider well depth, desired capacity, and maintenance requirements. Shallow well pumps are easier to maintain, while submersible pumps require professional service. Your choice will depend on your specific well characteristics and water needs.
Choosing the Right Well Pump
Selecting the right well pump is essential for guaranteeing an efficient and reliable water supply. The primary factor you'll need to ponder is your well's depth. For shallow wells under 25 feet, you'll want to use centrifugal or jet pumps. If your well is deeper than 110 feet, you'll need a submersible pump.
When replacing an existing pump, it's usually best to stick with the same type to maintain compatibility with your current system. Pay attention to the pump's GPM (gallons per minute) and PSI (pounds per square inch) ratings to guarantee it can provide the necessary flow and pressure for your water demand.
Don't make the mistake of oversizing your well pump, as this can lead to reduced performance and energy inefficiencies. Instead, match the pump's capacity to your water needs. If you're replacing an old pump, choose one with the same horsepower to guarantee a proper fit within your well casing.
Well Pump Sizing Guidelines
After considering the various factors in choosing the right well pump, it's important to focus on proper sizing. The size of your well is pivotal in determining the appropriate pump type. For shallow wells less than 25 feet deep, you'll need shallow well jet pumps. Deep well pumps or submersible pumps are necessary for wells between 25-400 feet.
When sizing your well pump system, consider your home's water demand. An average single-family home with 3-4 bedrooms typically requires a pump that can deliver 8-12 gallons per minute. Add 1 GPM for each additional water fixture. It's indispensable not to oversize your pump, as this can lead to reduced performance and energy inefficiency.
If you're replacing an existing pump, choose one with the same horsepower to maintain proper water pressure and flow. However, if you're transporting water over longer distances or to higher elevations, you may need a more powerful pump to overcome friction and vertical lift.
Essential Well Pump Accessories
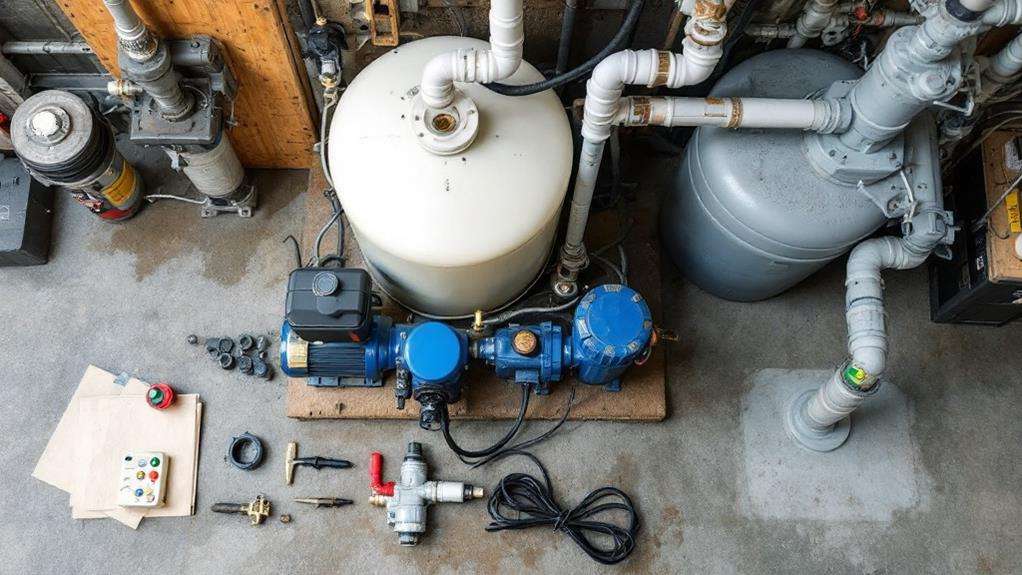

Well pump systems frequently require additional components to function ideally and protect your water supply. Pressure tanks are indispensable accessories that store water and maintain consistent pressure in your plumbing system when the pump isn't running. They work in tandem with pressure switches, which monitor the pressure in the tank and activate the pump when it drops below a preset level.
To secure a safe connection between your well casing and home plumbing, you'll need a pitless adapter. This device provides a watertight, freeze-proof seal that prevents contamination of your water supply. Check valves are another pivotal component, preventing backflow and ensuring water only flows from the well to your home.
For improved water quality and protection of your plumbing components, you may want to deliberate adding water filters and water softeners to your system. These accessories can remove impurities and reduce mineral buildup in your pipes and appliances.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
With your well pump and accessories selected, it's time to focus on proper installation and ongoing maintenance. You'll need to adhere to local building codes and manufacturer guidelines to guarantee your pump operates efficiently and reliably. Remember, submersible well pumps tend to require professional installation due to their complexity and location deep underground.
For deep well jet pumps or submersible pumps that are more than 25 feet below ground, you'll need to be particularly careful with installation. These pumps create a vacuum in the suction line, which is indispensable for proper water extraction. Shallow well jet pumps, on the other hand, need to be primed regularly to prevent air from entering the system.
To maintain your pump's performance, routinely check the pressure tank, clean the well screen, and inspect for leaks. Replace worn components like the foot valve and impeller as needed. For submersible pumps, it's best to consult a professional well service technician for maintenance and repairs, as they have the specialized equipment and skills required.
Troubleshooting Common Well Pump Issues
Even the most well-maintained well pump systems can encounter issues from time to time. As a Guide to understanding types of well pumps, it's vital to recognize common problems and their potential causes. If you're experiencing low water pressure, you'll need to check for a faulty pressure switch, tank waterlogging, or an improperly sized pump. These issues can affect various types of well pumps, including centrifugal pumps.
Frequent cycling of your water pump might indicate a leak in the plumbing system or a malfunctioning pressure tank. If your pump doesn't turn on, inspect the circuit breaker, pressure switch connections, and make sure it's receiving power. Unusual noises coming from your existing well pump could signal worn bearings, impeller issues, or motor problems.
Pay attention to your pump's temperature, as overheating may be caused by running dry, a malfunctioning thermal overload, or a failed capacitor. Regular maintenance of your well's air pressure and components is essential for best performance. By understanding these common issues and their potential causes, you'll be better equipped to troubleshoot problems with your well pump system and determine when professional assistance is needed.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Energy efficiency and cost savings go hand in hand when it comes to well pump systems. By properly sizing and maintaining your well pump, you can improve energy efficiency and reduce operating costs by up to 30%. Upgrading to a more efficient model, like a variable-speed drive submersible pump, can save you up to $300 annually on electricity bills.
To maximize energy efficiency, guarantee your pump is compatible with your property's depth and water demand. Regular servicing of components, including the pressure tank, can enhance the pump's performance. Proper system design is indispensable, involving selecting the right pump size and integrating it with storage tanks and pressure boosters to optimize overall energy usage.
You can achieve ongoing cost savings by monitoring your pump's energy consumption and making necessary adjustments. Consider factors like depth, water demand, and pressure requirements when choosing a pump. By focusing on energy efficiency through proper sizing, maintenance, and system design, you'll not only diminish your environmental impact but also enjoy significant long-term cost savings. Remember, an efficient well pump system benefits both your wallet and the environment.
