A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Heat Pump Systems
As a homeowner, you may not be fully aware of heat pump systems, which offer an energy-efficient and eco-friendly alternative to traditional HVAC. Heat pumps use thermal transfer to both heat and cool your home, providing year-round comfort. They're versatile, with ductless, geothermal, and air-source models available. Heat pumps can save you substantially on utility bills and reduce your carbon footprint. To maximize efficiency, you'll want to consider your property size, climate, and installation needs. Proper maintenance is key, but the benefits of heat pump technology make them a compelling choice over conventional systems. If you'd like to dive deeper into understanding how heat pumps work and their advantages, keep reading.
Key Takeaways
- A heat pump is an energy-efficient device that transfers heat between two environments, typically outside air/ground and the interior of a building.
- Heat pumps work by using thermal transfer mechanisms to absorb and concentrate heat, allowing them to efficiently heat and cool a home year-round.
- Common types of heat pump systems include ductless/mini-split, geothermal, and air-source models, each with unique installation requirements and suitability for different climates.
- Heat pumps offer significant energy savings and environmental benefits, with up to 300% efficiency and reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional HVAC systems.
- Proper sizing, installation, and regular maintenance are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency of a heat pump system.
What Is a Heat Pump?
A heat pump is an energy-efficient device that transfers heat between two environments, typically from the outside air or the ground to the interior of a building. It works by taking heat from a cooler area and transferring it to a warmer area, making it a versatile and environmentally-friendly heating and cooling solution. Heat pumps are particularly effective in areas with moderate climates, as they can efficiently handle seasonal variations in temperature.
Unlike traditional furnaces or air conditioners, heat pumps don't generate heat; instead, they move heat from one place to another. This process is remarkably efficient, often using up to 50% less energy than conventional heating and cooling systems. Additionally, heat pumps have a minimal environmental impact, as they don't produce direct greenhouse gas emissions. Whether you're looking to heat or cool your home, a heat pump system can be a smart and sustainable choice that can save you money on your energy bills while reducing your carbon footprint.
How Does a Heat Pump Work?
Now that you understand what a heat pump is, let's explore how it actually works. At the core, a heat pump moves heat from one place to another using thermal transfer mechanisms. By harnessing the laws of thermodynamics, heat pumps can achieve impressive thermal efficiency metrics compared to other heating and cooling systems.
The heat pump's compressor circulates refrigerant, absorbing heat from the outside air or ground and concentrating it. This heat is then transferred indoors, where it warms your home. In the summer, the process reverses, with the heat pump drawing heat from your home and expelling it outside, effectively cooling your living space.
The beauty of heat pump systems lies in their ability to operate in both heating and cooling modes, delivering year-round comfort with impressive energy efficiency. By understanding the underlying heat transfer mechanisms, you can appreciate the technological marvel that is the modern heat pump.
Types of Heat Pump Systems
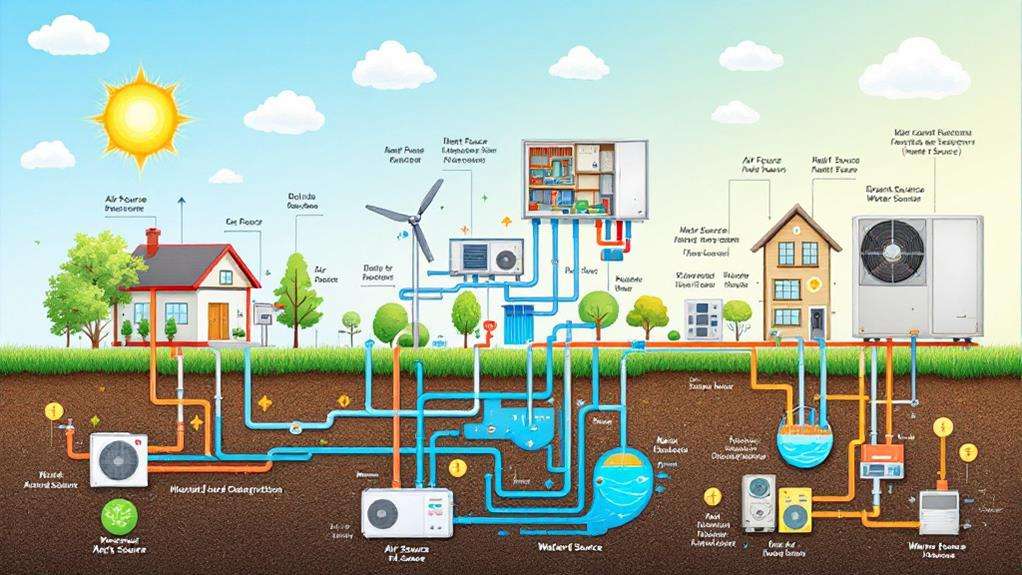
Although heat pumps share a common operating principle, there are several distinct types that cater to different heating and cooling needs. Ductless heat pumps, also known as mini-split systems, are a popular choice for homes or businesses without existing ductwork. They consist of an outdoor compressor unit and one or more indoor air-handling units, allowing you to control the temperature in specific rooms or zones. Geothermal heat pumps, on the other hand, utilize the stable temperatures found underground or in bodies of water to provide highly efficient heating and cooling. These systems require the installation of a ground loop, but they can offer significant energy savings compared to traditional HVAC systems. Other heat pump varieties include air-source, hybrid, and water-source models, each with its own advantages and applications. The type of heat pump that's right for you will depend on factors like the size and layout of your space, your climate, and your energy efficiency goals.
Benefits of Heat Pump Systems
One of the primary benefits of heat pump systems is their energy efficiency. Unlike traditional heating and cooling systems that rely on fossil fuels, heat pumps simply transfer heat from one place to another, making them a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly option. By using renewable energy sources, such as the air or ground, heat pumps can provide heating and cooling at a fraction of the cost of traditional systems.
Furthermore, heat pump systems can significantly reduce your carbon footprint. Since they don't rely on combustion, they produce zero direct greenhouse gas emissions, making them a much greener choice for your home or business. This not only benefits the environment but can also lead to substantial cost savings on your energy bills over time.
Whether you're looking to save money or reduce your environmental impact, investing in a heat pump system is an excellent choice that can provide you with reliable and efficient heating and cooling for years to come.
Selecting the Right Heat Pump

When selecting the right heat pump for your home or business, there are several key factors to consider. The size of the unit is crucial, as it must be properly sized to efficiently heat and cool your space. You'll also need to consider the climate suitability, as different heat pump models perform better in specific temperature ranges.
- Evaluate your heating and cooling needs based on the size and layout of your property. Choosing the right capacity is essential for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
- Research the climate in your region and select a heat pump designed to operate effectively in your local weather conditions, whether that's a mild, temperate climate or a more extreme, cold-weather environment.
- Consider the efficiency ratings, such as SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor), to ensure you're getting a high-performing and energy-saving unit.
- Determine if you need a single-stage or variable-speed heat pump, as the latter can provide better temperature control and further energy savings.
- Don't forget to factor in installation costs and any necessary ductwork or electrical upgrades to ensure a seamless and successful integration into your home or business.
Installation and Maintenance
Properly installing your heat pump is critical for its efficient and long-lasting performance. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully, and ensure your contractor adheres to local building codes and industry best practices. Improper installation can lead to decreased efficiency, premature wear, and even safety hazards.
Once installed, regular maintenance is a must. Regularly clean or replace air filters to maintain airflow. Inspect and clean the outdoor unit, removing any debris or vegetation that could obstruct airflow. Regularly check refrigerant levels and top up as needed. Ensure all electrical connections remain tight and secure. Consider scheduling an annual tune-up with a qualified HVAC technician to catch any potential issues before they become major problems.
Staying on top of proper installation procedures and routine maintenance requirements will help your heat pump operate at peak efficiency for years to come. With a little diligence, you can enjoy the comfort and cost savings of your heat pump system for the long haul.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Heat pumps are highly energy-efficient systems, but you can take several steps to maximize their performance. By understanding the energy efficiency considerations, you can reduce your energy costs and ensure your heat pump operates at its best.
- Ensure your heat pump is properly sized for your home. An oversized or undersized unit will not run efficiently, leading to higher energy bills.
- Regularly maintain your heat pump by cleaning the filters, coils, and other components. This will keep it running smoothly and prevent any performance issues.
- Insulate your home properly to minimize heat loss or gain, reducing the workload on your heat pump and improving its efficiency.
- Consider using a programmable thermostat to automatically adjust the temperature settings when you're away or sleeping, further reducing energy consumption.
- Explore the possibility of upgrading to a more energy-efficient heat pump model if your current one is outdated or not performing well.
Advantages Over Traditional HVAC
One key advantage of heat pump systems over traditional HVAC is their energy efficiency. Heat pumps use electricity to move heat rather than generating it, making them significantly more efficient. This translates to substantial energy savings, cutting your utility bills and reducing your carbon footprint. Compared to traditional furnaces or air conditioners, heat pumps can offer up to 300% efficiency, meaning you get three times the energy output for the same electricity input.
Furthermore, heat pumps have a smaller environmental impact. By minimizing fossil fuel consumption, they contribute less to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable, eco-friendly home solutions. Heat pump systems also eliminate the need for combustible fuels, enhancing safety and eliminating the risk of carbon monoxide leaks. Overall, the energy savings and environmental benefits of heat pumps make them a compelling choice over traditional HVAC systems.
